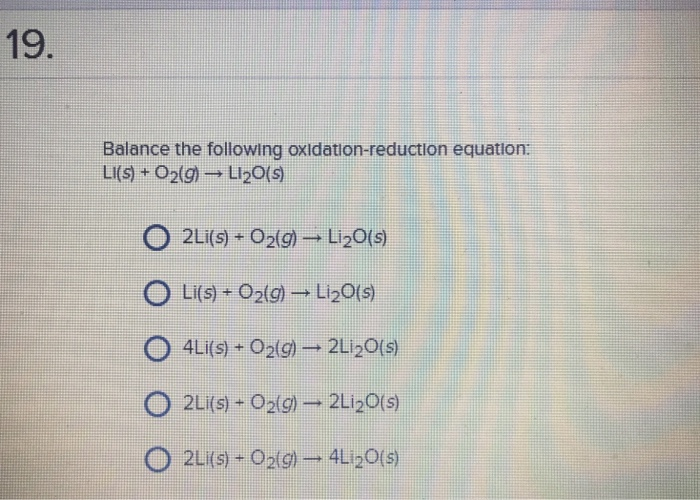
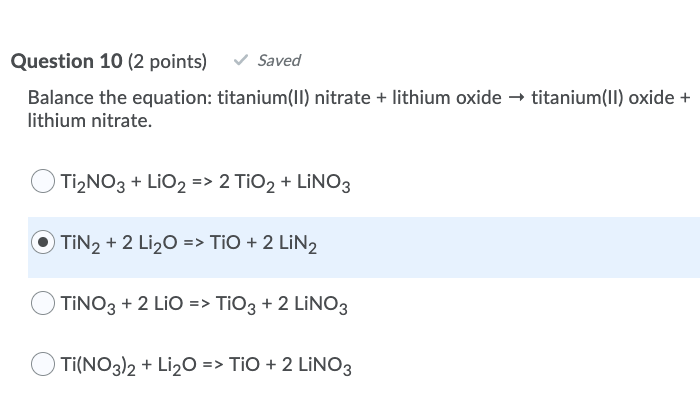
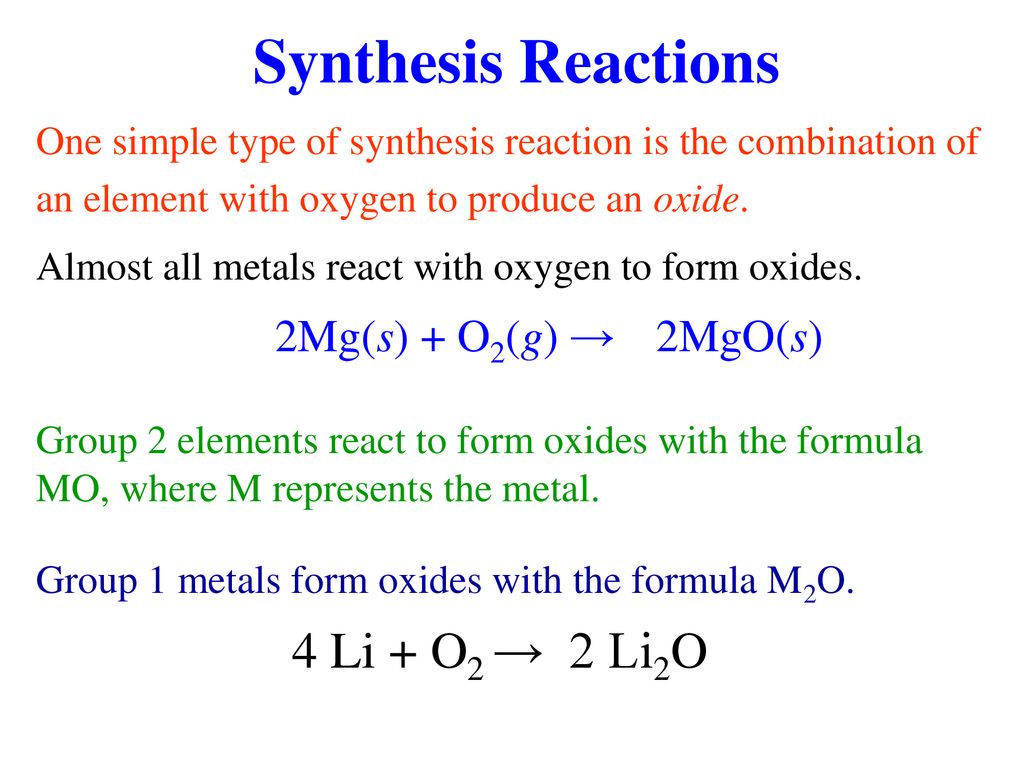
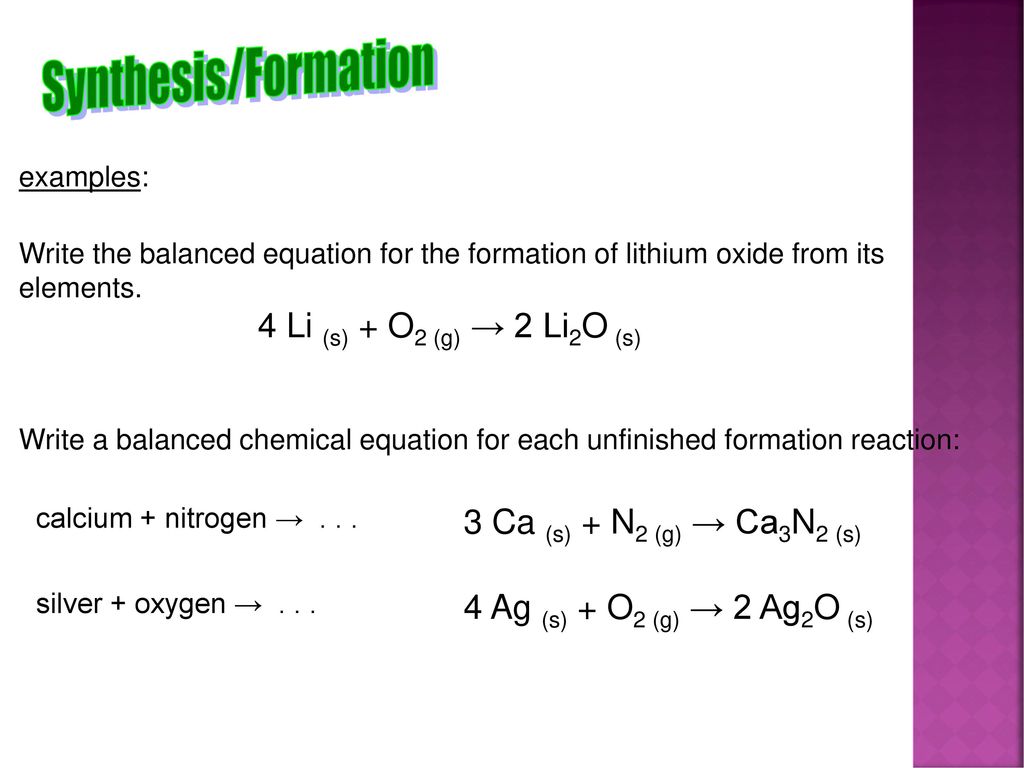
WARM UP 4 Li + O2 2 Li2O If you have 804 g of Li available for the reaction, calculate the amount of O2 you will need to pump into the

SOLVED: 3 Lithium reacts with oxygen to produce lithium oxide according to the following equation: 4 Li (s) + 02 (g) - 2 LizO (s) How many moles of oxygen are needed

Lithium Peroxide Growth in Li–O2 Batteries via Chemical Disproportionation and Electrochemical Mechanisms: A Potential-Dependent Ab Initio Study with Implicit Solvation | The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
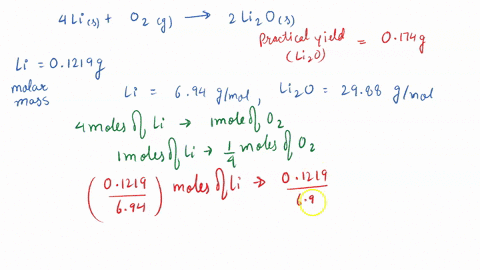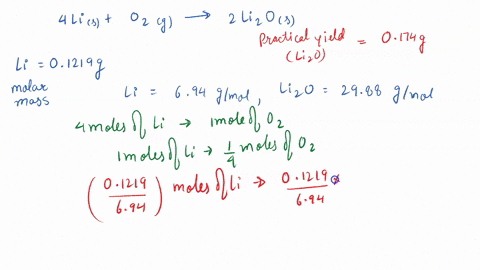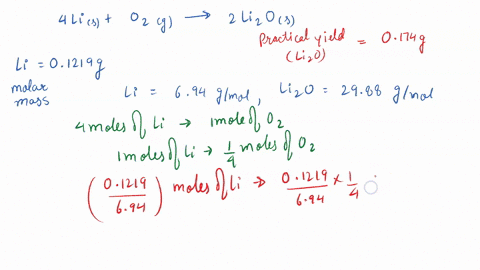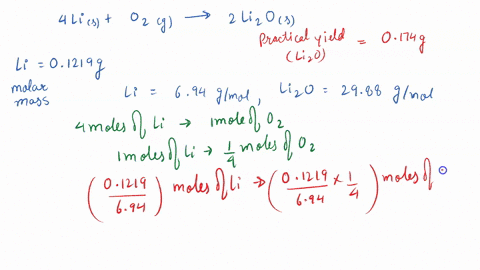
SOLVED: 3 Lithium reacts with oxygen to produce lithium oxide according to the following equation: 4 Li (s) + 02 (g) - 2 LizO (s) How many moles of oxygen are needed